The Window class represents a window in the
Boson Application. It provides a way to
manage window, including their properties, events, state, and associated
WebView.
#Main Window
The Application::$window property provides convenient access to the
main window of the application.
This is a facade property that internally accesses the default window inside the window manager.
$app = new Boson\Application(); // Access the main window $window = $app->window;
If the main window is closed, the next available window from window manager will become the main window.
If you try to access the
$windowproperty after the all windows has been closed, aNoDefaultWindowExceptionwill be thrown.
The main window already available by default in any application.
#Title
Contains title of the specified window encoded as UTF-8. The window title can
be in any language and even include emojis. All line breaks (\n)
and similar characters will be removed.

To get the window title, simply read this property. The title will contain the
real value, including all invisible (like \n) characters.
$title = $window->title; echo 'Window Title: ' . $title;
To update the window title, set a new value to the property.
$window->title = 'New Window Title!';
Indirect modification of
Window::$titleis not allowed, which means that this property cannot be passed by reference.$title = &$window->title; // ❌ not available
Window title change also fires a corresponding event that can be subscribed to using the event system.
#State
Each window has several states. The window can be minimized, maximized to full screen, or in a normal state.
To get the current state of a window, you can use the Window::$state
property.
echo 'Window State: ' . $window->state->name;
This property will contain one of the possible values of
Boson\Window\WindowState enum.
enum WindowState { /** * Standard window state with custom (user defined) sizes. */ case Normal; /** * Maximized (i.e. zoomed) window state. */ case Maximized; /** * Minimized (iconified) window state. */ case Minimized; }
There are corresponding methods for changing states from code.
Window state change also fires a corresponding event that can be subscribed to using the event systemm.
#Minimize
In order to minimize the window, you should use the appropriate
Window::minimize() method.
// Minimize window to tray $window->minimize();
When restoring a window from the tray using the operating system features
(for example,
Normal
- Window state is
Normal. - Execute
$window->minimize() - Restore using OS features (like Alt + Tab).
- Window state is again
Normal.
Maximized
- Window state is
Maximized. - Execute
$window->minimize() - Restore using OS features (like Alt + Tab).
- Window state is again
Maximized.
#Maximize
In order to maximize the window, you should use the appropriate
Window::maximize() method.
// Maximize window from tray or normal state $window->maximize();
#Restore
In order to restore the window state (that is, switch to a Normal
state), you should use the appropriate Window::restore() method.
// Restore window state $window->restore();
#Visibility
The Window::$isVisible property controls the visibility state of the window.
It allows you to show or hide the window programmatically.
It is also worth noting that the initial state of the window visibility depends on the window settings. By default, the window is shown.
To check if a window is currently visible:
if ($window->isVisible) { echo 'Window is visible'; } else { echo 'Window is hidden'; }
The visibility state is independent of the window's
Minimized/Maximizedstate. A window can be visible whileMinimizedor hidden whileMaximized.Hidden windows are not displayed in the tray and cannot be restored using the OS functionality.
#Show
To show the window you may use desired Window::show() method.
// Show the window $window->show();
You can also show the window through a
Window::$isVisibleproperty. To do this, simply set thetrue.// Show the window $window->isVisible = true;
#Hide
To hide the window you may use desired Window::hide() method.
// Hide the window $window->hide();
You can also hide the window through a
Window::$isVisibleproperty. To do this, simply set thefalse.// Hide the window $window->isVisible = false;
#Decorations
The Window::$decoration property allows you to control the
window's appearance and style.
// Get current decoration mode echo $window->decoration->name;
It supports different decoration modes defined in the
Boson\Window\WindowDecoration enum.
enum WindowDecoration { /** * Default window style. */ case Default; /** * Default window style with preferred dark mode. */ case DarkMode; /** * A "frameless" windows is a window which hides the default * window buttons & handle assigned to it by the operating system. */ case Frameless; /** * Enables "frameless" mode and makes the window completely transparent */ case Transparent; }
Let's say we load the content as <div style="background: #fff">Hello World!</div>
in webview. So the result with different decorations will look like this.
Default
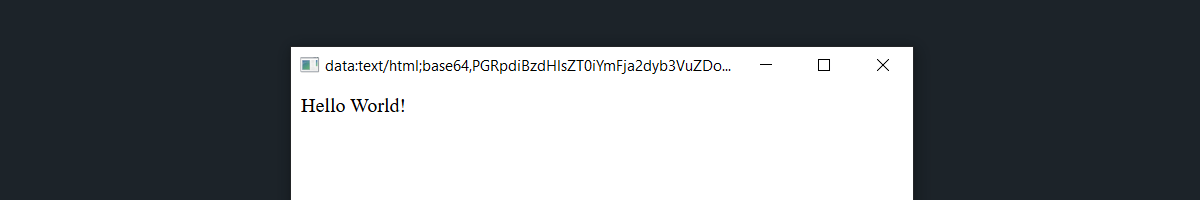
DarkMode*
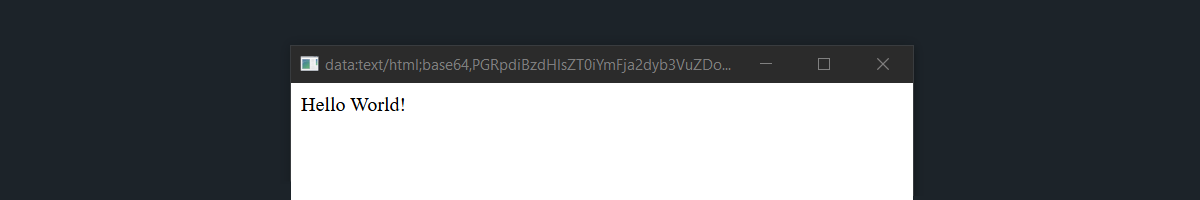
Frameless

Transparent

Window decoration change also fires a corresponding event that can be subscribed to using the event system.
#Default
The standard window style with system default appearance (title bar, close, minimise and maximise buttons).
$window->decoration = WindowDecoration::Default;
#Dark Mode
Default window style with dark theme preference.
$window->decoration = WindowDecoration::DarkMode;
#Frameless
A frameless window hides the default window decorations (title bar, buttons) provided by the operating system.
$window->decoration = WindowDecoration::Frameless;
You can use the Minimize, Maximize, Restore, Close, Drag and Resize features to implement window controls manually.
When using frameless (or transparent) windows, you need to implement your own window controls and drag regions using HTML attributes.
#Transparent
Enables frameless mode and makes the window background transparent.
$window->decoration = WindowDecoration::Transparent;
With transparent windows, you should use CSS to control the background color:
<style> body { background: rgba(255, 255, 255, .8); } </style> <body> Content </body>
You can use the Minimize, Maximize, Restore, Close, Drag and Resize features to implement window controls manually.
#Size
The window size can be controlled through several properties that allow you to manage the current size, minimum and maximum bounds of the window.
#Current Size
The Window::$size property provides access to the current window
dimensions. The object in the window is mutable which allows both
reading and updating the size.
// Get current size echo $window->size; // Size(640 × 480) // Update width and height separately $window->size->width = 800; $window->size->height = 600; // Update both dimensions simultaneously $window->size->update(800, 600); // Set size using Size object $window->size = new Boson\Window\Size(800, 600);
Window dimensions must be non-negative
int32(an integer value between 0 and 2147483647).Attempting to set values outside this range will result in an exception.
Window resize also fires a corresponding event that can be subscribed to using the event system.
#Minimum Size
The Window::$min property controls the minimum allowed dimensions
of the window. Users cannot resize the window smaller than these values.
// Get minimum size echo $window->min; // Size(0 × 0) // Set minimum size separately $window->min->width = 400; $window->min->height = 300; // Or update all dimensions at once $window->min->update(400, 300);
Setting minimum size helps prevent the window from being resized too small, which could make the content unreadable or unusable.
Window min size must be non-negative
int32(an integer value between 0 and 2147483647).Attempting to set values outside this range will result in an exception.
#Maximum Size
The Window::$max property controls the maximum allowed dimensions
of the window. Users cannot resize the window larger than these values.
// Get maximum size echo $window->max; // Size(3840 × 2160) // Set maximum size $window->max->width = 1920; $window->max->height = 1080; // Or update both at once $window->max->update(1920, 1080);
The maximum size is typically limited by the screen resolution. Setting a value larger than the screen size may not have the desired effect.
Linux/GTK4
Not supported because X11-specific functions such as
gtk_window_set_geometry_hintswere removed.This option has no effect.
Window max size must be non-negative
int32(an integer value between 0 and 2147483647).Attempting to set values outside this range will result in an exception.
#Resizing
The Window::startResize() method allows you to programmatically
start resizing the window. This is particularly useful for frameless windows
where you need to implement custom window controls.
The method takes one of the available arguments:
Boson\Window\WindowCorner- window corner.Boson\Window\WindowEdge- window edge.
// Start resizing the window on the right side $window->startResize(Boson\Window\WindowEdge::Right); // Start resizing the window on the bottom-left side $window->startResize(Boson\Window\WindowCorner::BottomLeft);
The end of the resizing occurs on the mouse up event at any place therefore, it is recommended to call this method when mouse down on any element.
$app = new Boson\Application(); $app->webview->functions->bind('resize', function () use ($app) { $app->window->startResize( Boson\Window\WindowCorner::BottomRight, ); }); $app->webview->html = <<<'HTML' <div onmousedown="resize()"> Press + hold to resize the window! </div> HTML;
#Resize via HTML
You can also use the data-webview-resize HTML attribute
to implement the window resize functionality.
Possible values for window edges:
t- Top resize edge handle.b- Bottom resize edge handle.l- Left resize edge handle.r- Right resize edge handle.
Possible values for window corners:
tr- Top-Right resize corner handle.br- Bottom-Right resize corner handle.bl- Bottom-Left resize corner handle.tl- Top-Left resize corner handle.
<button data-webview-resize="t"> ↑ </button> <button data-webview-resize="l"> ← </button> <button data-webview-resize="tr"> ↗ </button> <button data-webview-resize="bl"> ↙ </button>
To prevent this event for child HTML elements, use the
data-webview-ignoreHTML attribute.<!-- header resizes the window --> <header data-webview-resize="l"> <span>Custom Title Bar</span> <!-- except close button --> <button data-webview-ignore>Close</button> </header>
For standard windows with decorations, resizing is handled automatically by the operating system through the window corners and edges.
#Dragging
The Window::startDrag() method allows you to programmatically start
dragging the window. This is particularly useful for frameless windows where you
need to implement custom window controls.
// Start dragging the window $window->startDrag();
The end of the drag occurs on the mouse up event at any place therefore, it is recommended to call this method when mouse down on any element.
$app = new Boson\Application(); $app->webview->functions->bind('drag', function () use ($app) { $app->window->startDrag(); }); $app->webview->html = <<<'HTML' <div onmousedown="drag()"> Press + hold to drag the window! </div> HTML;
#Drag via HTML
You can also use the data-webview-drag HTML attribute to make
specific elements draggable.
<header data-webview-drag> <span>Custom Title Bar</span> </header>
To prevent this event for child HTML elements, use the
data-webview-ignoreHTML attribute.<!-- header is draggable --> <header data-webview-drag> <span>Custom Title Bar</span> <!-- except close button --> <button data-webview-ignore>Close</button> </header>
For standard windows with decorations, dragging is handled automatically by the operating system through the title bar.
#Focus
Windows can be given input focus and brought to the front with
Window::focus() method.
// Focus the window $window->focus();
Linux/GTK4
There is no way to artificially focus the window.
This method has no effect.
Keep in mind that it can be very disruptive to the user when a window is forced to the top. Please use this feature judiciously.
Window focus also fires a corresponding event that can be subscribed to using the event system.
#Always On Top
The Window::$isAlwaysOnTop property allows you to control whether
a window should stay on top of other windows. When enabled, the window will
remain visible even when other windows are in focus.
// Check if window is always on top if ($window->isAlwaysOnTop) { echo 'Window is always on top'; } else { echo 'Window is not always on top'; } // Enable always on top $window->isAlwaysOnTop = true; // Disable always on top $window->isAlwaysOnTop = false;
Linux/GTK4
There is no way to artificially set window always on top.
This method has no effect.
Windows that are always on top may interfere with normal window management and user interaction. Please use this feature judiciously.
#Click Through
The Window::$isClickThrough property allows you to control
whether a window should intercept mouse events. When enabled, mouse clicks
will pass through the window to the windows or applications behind it.
Mouse events are not intercepted not only through the internal OS (Windows, Linux, macOS, etc...) API, but also through JavaScript. The system buttons to minimize, maximize or close also do not respond to clicks.
// Check if window is click-through if ($window->isClickThrough) { echo 'Window does not intercept mouse events'; } else { echo 'Window intercepts mouse events'; } // Enable click-through feature $window->isClickThrough = true; // Disable click-through feature $window->isClickThrough = false;
When "click-through" is enabled:
- The window cannot be moved, resized, or focused by clicking.
- All mouse events will be ignored.
- The window will effectively become a visual overlay only.
This functionality may be unpleasant for the user. Please use this feature judiciously.
#Window Close
The Window::close() method allows you to close and destroy a
window and its associated resources. This operation is irreversible - once a
window is closed, it cannot be reopened.
// Close the window $window->close();
Closing a window is a destructive operation. All resources associated with the window, including its WebView, will be freed.
Any attempts to use the window (except
Window::$isClosedproperty) after closing will result in undefined behavior.
You can check if a window is closed using the $isClosed property:
if ($window->isClosed) { echo 'Window is already closed'; } else { $window->close(); }
Window closing also fires a corresponding event that can be subscribed to using the event system.
#Identifier
The Boson\Window\WindowId is a unique identifier for each window
in the application. The identifier is needed to compare different windows
for their equivalence.
To get window identifier use the Window::$id property.
$app = new Boson\Application(); echo 'ID: ' . $app->window->id;
An identifier is a value object and contains methods for comparison and conversion to scalars.
if ($window1->id->equals($window2->id)) { echo sprintf('The %s is equals to %s', $window1, $window2); }
The
WindowIdis automatically generated when a window is created and remains constant throughout the window's lifetime.
The identifier consists of two parts:
- A unique integer value that identifies the window in the application.
- A pointer to the native window handle.
Please do not use the second
WindowIdargument unless you are sure. It provides unsafe access to the window handle pointer, for working with low-level API.
In addition to the ability to convert to a string (i.e. implementations of the
Stringable interface), this identifier can also be converted to an
64-bit (or 32-bit on 32-bit OS) signed integer, which represents the actual
physical address of the window pointer.
echo $window->id->toInteger();
Technically, this behaviour can be used to pass a window pointer to subprocesses and then restore the pointer from it, like:
// process-1 // somehow pass the scalar addr to the process-2 $addr = $window->id->toInteger(); // process-2 // somehow get a scalar addr value $handle = $ffi->cast('saucer_handle*', $addr);However, please note that this may cause ownership issues and should be used with caution.
